Literature Review AI (LiRA)
An AI-powered tool to assist with your PubMed literature review process.
Download and extract the contents of the zip file to a temporary folder, and run lirapkg.exe within the folder to install Literature Review AI.
Due to the high cost of digital code signing, LiRA is provided 'as is,' which may trigger a "security warning from Windows during installation. The writer of the software, who is a medical doctor, personally assures that LiRA is free of viruses, malware, and unwanted software. Nonetheless, users should exercise their due diligence by inspecting LiRA locally or online by an antivirus software.
Download Literature-Review-AI.Windows.zipBy downloading, you agree to our Privacy Policy
Literature Review AI: a Novel Tool for Automating PubMed Literature Reviews
Literature Review AI (LiRA) is a computer program designed to aid in literature review on PubMed by enabling automatic searching, downloading, and analysis of indexed articles. The program is not intended to replace manual reviews but to precede them, enabling a quick assessment of a study's usefulness. We strongly recommend that a conventional literature review follow the automated process to both validate LiRA's performance and ensure due diligence.
Overview
LiRA is a downloadable software that runs on personal computers. It provides a graphical user interface (Figure 1) containing three screens - one (Config Helper) for configuring the tool, one (PubMed Helper) for performing automatic searching and downloading of PubMed articles, and one (AI Helper) for accomplishing AI-based analysis of downloaded abstracts. This document uses the terms 'abstract' and 'citation' interchangeably.
Config Helper
Config Helper requires four fields: Entrez Email, Entrez API Key, OpenAI API Key, and Output Folder. Entrez Email is the user's email registered with the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) to obtain a software key. Entrez API Key is a software key provided by NCBI for use with their software library (1). OpenAI API Key is a software key provided by OpenAI for use with their application programming interface (API) (2). Finally, Output Folder refers to a local folder designated by the user to store downloaded abstracts.
PubMed Helper
PubMed Helper contains three input fields, including Search Criteria, Referenced Abstracts, and Similar Abstracts. Search Criteria is required and equivalent to the search box on PubMed. Referenced Abstracts and Similar Abstracts are optional settings to specify whether to download referenced or similar abstracts. The downloaded abstracts are saved individually in '.txt' files for visualization, and collectively in a '.csv' (comma separated value) file for automated submission to OpenAI.
AI Helper
AI Helper contains three input fields, namely Abstracts Folder, Instructions to AI, and Response Type. Abstracts Folder is the location where citations are stored for a given search. Each search in PubMed Helper creates its own Abstracts Folder. Instructions to AI, is self-explanatory. Lastly, Response Type indicates whether the user's instructions to AI generates a boolean ('yes/no') or descriptive text. For boolean responses, the matched citations are copied to a separate folder, where file names begin with 'yes' or 'no.' For descriptive responses, all citations are copied to a separate folder, where each file contains the original text with the AI response prepended.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages include time-saving, automatic downloading of both referenced and similar articles, automatic AI-based analysis of downloaded citations, minimization of human error, removal of duplicate citations, and automatic sorting of citations by date in a descending order.
Disadvantages include analysis limited to PubMed citations, which are predominantly abstracts rather than full-length articles, and a cost component paid directly to OpenAI by LiRA users.
To the best of the authors' knowledge, no tools comparable to LiRA currently exist, underscoring its novelty.
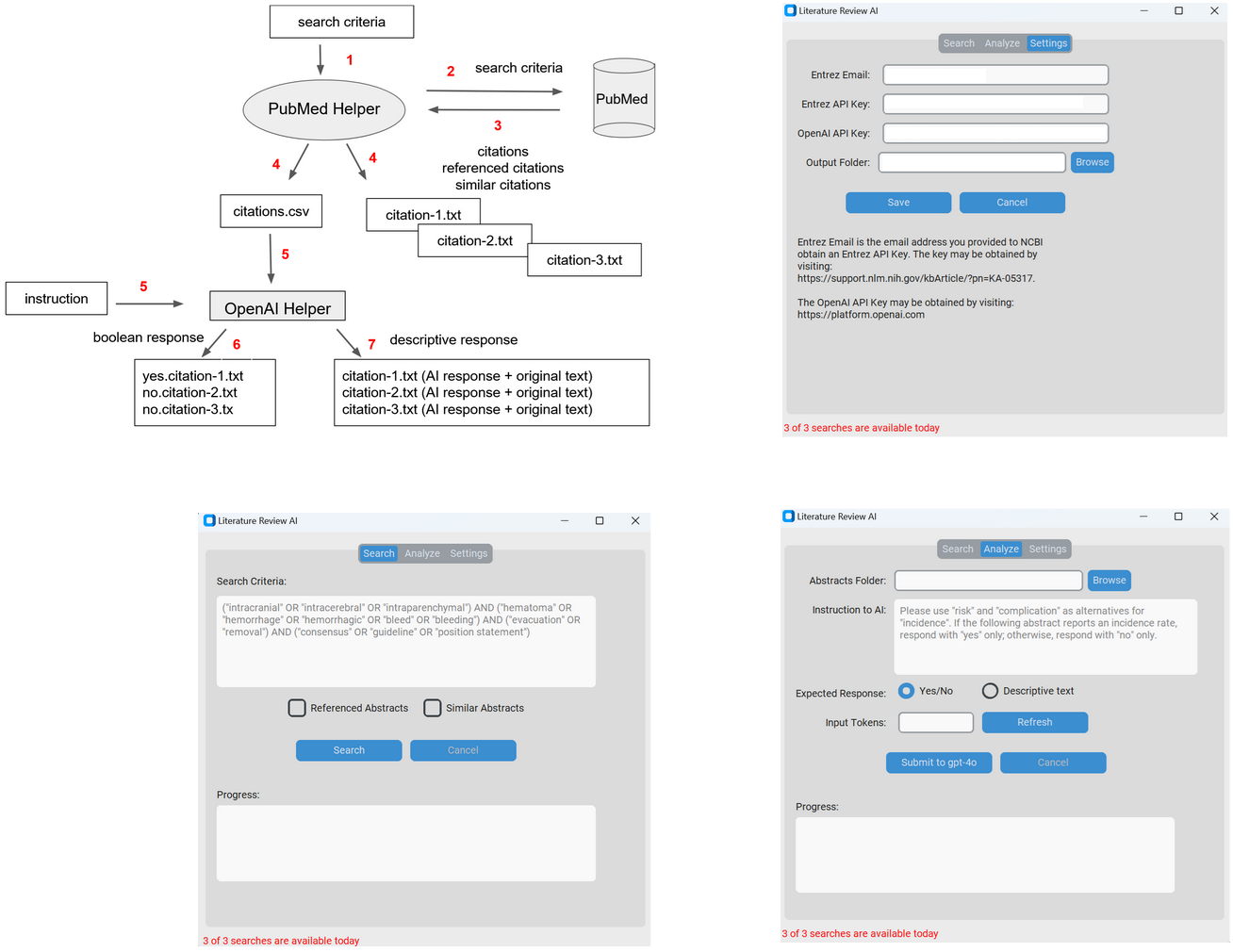
Figure 1: Screenshots of LiRA architecture, Config Helper, PubMed Helper, and AI Helper.